Do not index
Do not index
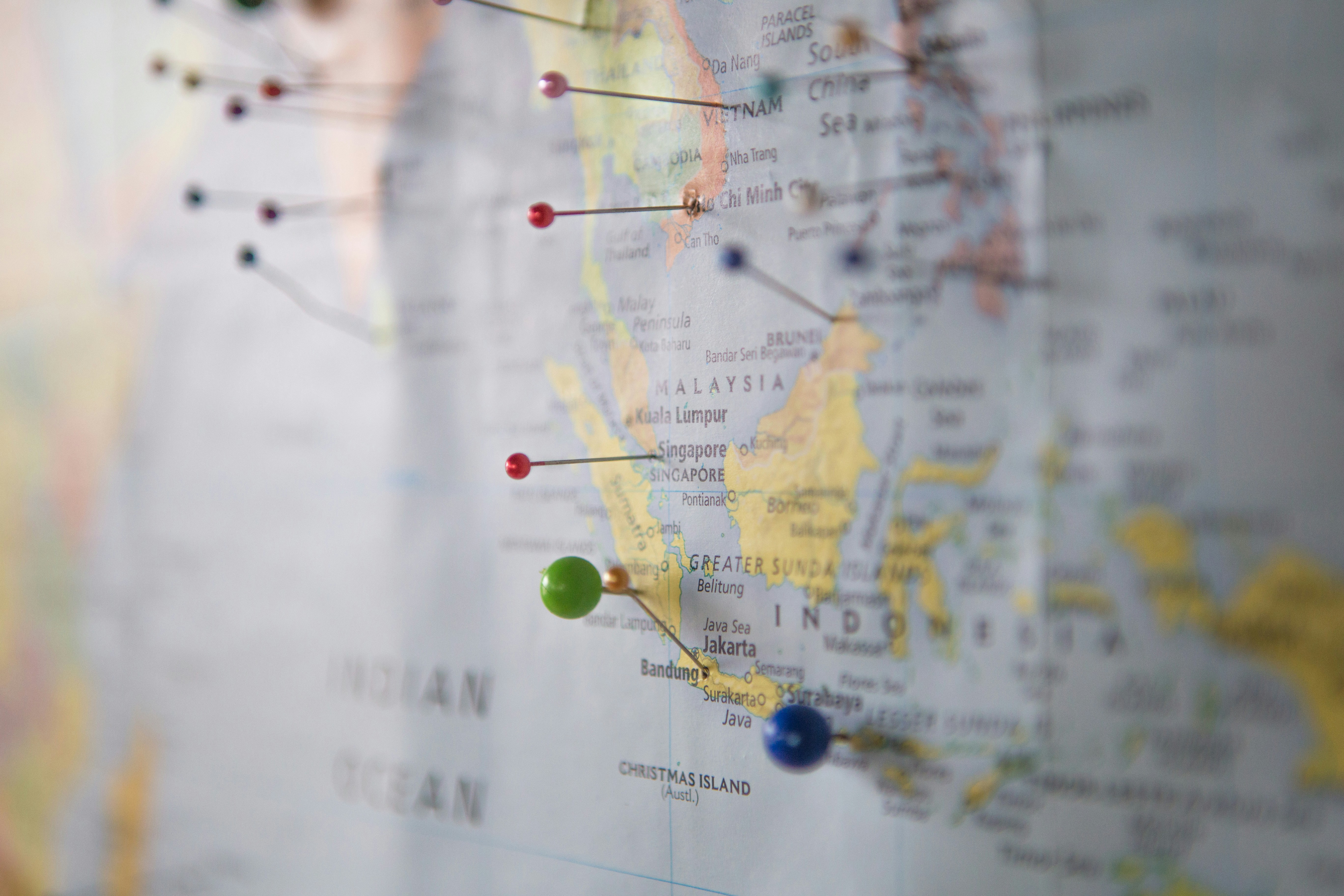
In today's globalized world, the video game industry has expanded far beyond the borders of its country of origin. With an increasingly diverse audience, the importance of localization in gaming has become paramount. Localization goes beyond mere translation—it involves adapting a game's content, visuals, and audio to cater to the cultural nuances and preferences of a target region. In this blog post, we will discuss the significance of localization in gaming and how it helps bridge cultural gaps, enhance player experience, and ultimately boost a game's success in international markets.
Enhancing Player Experience
One of the primary reasons for localizing a game is to provide players with an engaging and immersive experience. By adapting the game's language, visuals, and audio to suit the target audience's cultural sensibilities, developers can ensure that players can relate to and enjoy the game more effectively (1). A well-localized game can create a sense of familiarity for the players, increasing their connection to the game world and its characters (2).
Increasing Market Reach
Localization plays a crucial role in expanding a game's market reach. By tailoring the game to the preferences of various regions, developers can tap into new markets and increase their potential audience (3). This not only boosts sales but also enhances a game's global visibility and strengthens its brand presence (4).
Improving Cultural Sensitivity
Localization is an essential process to ensure that a game's content is culturally sensitive and does not unintentionally offend players from different regions. Developers must consider cultural norms, taboos, and preferences to avoid controversies that could negatively impact the game's reception and sales (5). A well-localized game demonstrates a commitment to respecting the target audience's culture and values (6).
Facilitating Community Building
A localized game enables players to communicate and interact with each other in their native language, fostering a sense of community and camaraderie among players (7). Localization can help create a welcoming environment for players from diverse backgrounds, encouraging them to share their experiences and build lasting connections within the gaming community (8).
Boosting Financial Success
Localized games have a higher likelihood of achieving financial success in international markets. A study conducted by the European Parliament found that localized games could increase sales by up to 67% in some European countries (9). By investing in localization, developers can maximize their returns and enhance their games' overall profitability (10).
Conclusion
In conclusion, localization is an integral aspect of the gaming industry, essential for breaking cultural barriers and building bridges between diverse audiences. By investing in localization, developers can create immersive and culturally sensitive gaming experiences, expand their market reach, and ultimately boost their games' financial success. As the gaming industry continues to grow and evolve, the importance of localization will only become more pronounced, making it a critical component in the success of any game.
As the gaming industry continues to flourish and cater to an increasingly diverse audience, localization remains a vital aspect of development. By prioritizing localization, game developers can foster connections among players worldwide, bridge cultural gaps, and ultimately, ensure the success of their games on a global scale.
References:
- Chandler, H. M. (2005). The Game Localization Handbook. Hingham, MA: Charles River Media.
- Ibid.
- O'Hagan, M., & Mangiron, C. (2013). Game Localization: Translating for the Global Digital Entertainment Industry. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company.
- Ibid.
- Esselink, B. (2000). A Practical Guide to Localization. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company.
- Ibid.
- Edwards, J. (2011). The Importance of Localization in Online Gaming. Gamasutra. Retrieved from https://www.gamasutra.com/view/feature/134586/the_importance_of_localization_in_.php
- Ibid.
- European Parliament (2012). The Video Games Industry. Retrieved from https://www.europeanparliament.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/note/join/2012/462453/IPOL-CULT_NT(2012)462453_EN.pdf
- 10. Mangiron, C., & O'Hagan, M. (2006). Game Localisation: Unleashing Imagination with 'Restricted' Translation. The Journal of Specialised Translation, 6, 10-21. Retrieved from https://www.jostrans.org/issue06/art_ohagan.php
.jpeg)